Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
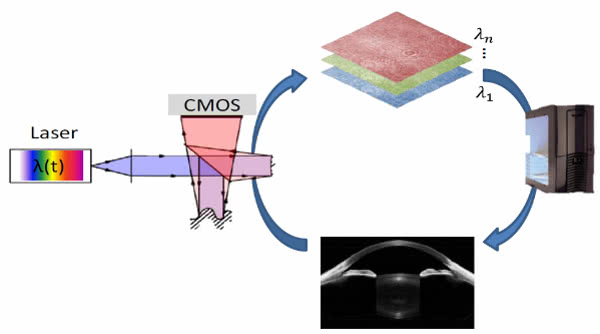
Multi-MHz-OCT
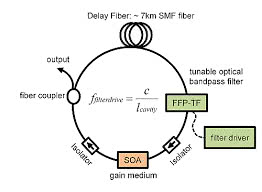
High-speed OCT with several million A-scans per second. This allows complete volumes with video rate in real time. The source used is a swept-source FDML lasers. Cardiovascular structures or very large areas of the retina (wide field) can thus be displayed with no movement artifacts.
Full-Field-OCT / Holoscopy
In contrast to conventional, scanning OCT systems, the measured objects are not scanned in the case of volume acquisitions, but illuminated in a planar manner. Due to the parallelization phase-stable volumetric images are possible when measuring speed is sufficient.
As a result, many problems that are solved in the conventional OCT with elaborate setups can now be solved numerically during the data reconstruction, for example, the correction of a defocusing or other aberrations.
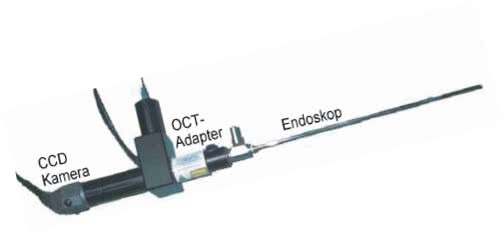
Endoscopic OCT
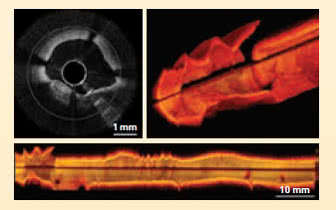
By coupling an OCT system to an endoscope, images of the body interior, e.g. the bladder can be accomplished.
Functional OCT
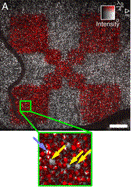
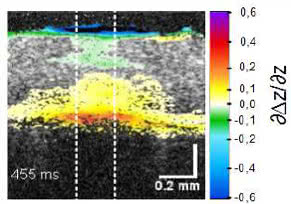
For functional imaging, successive image sequences are used to calculated and visualize smallest changes in refractive index or nanometer motion, e.g. blood flow (angiography) or expansions (pulse wave of vessels or temperature increases)